 Smoothy Slim
Smoothy Slim
 Smoothy Slim
Smoothy Slim

 Photo: Marta Dzedyshko
Photo: Marta Dzedyshko
Body odor is caused by a mix of bacteria and sweat on your skin. Your body odor can change due to hormones, the food you eat, infection, medications or underlying conditions like diabetes. Prescription-strength antiperspirants or medications may help.

Cucumbers are considered as extremely low-calorie foods made up of 96% water. 100 grams of cucumbers add up to just 45 calories. They are packed...
Read More »
No, you can't run out of sperm. Your testes are always making new sperm, which means you'll have a constant supply even if you're masturbating a...
Read More »
Made into a potent powdered supplement blended right into water or your favorite beverage to be appreciated as a scrumptious morning smoothy.
Learn More »Overview What is body odor? Body odor is what you smell when your sweat comes in contact with the bacteria on your skin. Sweat itself doesn’t smell, but when the bacteria on your skin mix with your sweat, it causes an odor. Body odor can smell sweet, sour, tangy or like onions. The amount you sweat doesn’t necessarily impact your body odor. That’s why a person can have an unpleasant body odor but not be sweaty. Conversely, a person can sweat excessively but not smell. This is because body odor is a result of the type of bacteria on your skin and how that bacteria interacts with sweat, not the sweat itself. Sweating is the secretion of fluids by sweat glands onto your skin’s surface. There are two types of sweat glands: eccrine and apocrine. Apocrine glands are responsible for producing body odor. Eccrine glands Eccrine glands secrete sweat directly to the surface of your skin. As the sweat evaporates, it helps cool your skin and regulate your body temperature. It doesn’t produce a smell. When your body temperature rises due to physical exertion or being hot, the evaporation of sweat from your skin produces a cooling effect. Eccrine glands cover most of your body, including palms and soles. Apocrine glands Apocrine glands open up into your hair follicles. Hair follicles are the tube-like structure that keeps your hair in your skin. You can find apocrine glands in your groin and armpits. These glands produce sweat that can smell when it comes in contact with bacteria on your skin. Apocrine glands don’t start working until puberty, which is why you don’t smell body odor in young children. Sweating is a natural body process, but due to certain foods we eat, hygiene practices or genetics, sweat can have a bad smell once it comes into contact with your skin. Changes in the amount you sweat or the smell of your body odor could indicate a medical condition. Who is more likely to experience foul body odor? Men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB) have more frequent problems with body odor because they have more hair (so they have more apocrine glands). Apocrine glands become active once a person reaches puberty, so body odor doesn’t begin until adolescence. Possible Causes What causes body odor? Body odor happens when bacteria on your skin come in contact with sweat. Our skin is naturally covered with bacteria. When we sweat, the water, salt and fat mix with this bacteria and can cause odor. The odor can be bad, good or have no smell at all. Factors like the foods you eat, hormones or medications can affect body odor. A condition called hyperhidrosis makes a person sweat excessively. People with this condition may be more susceptible to body odor because they sweat so much, but it’s often the eccrine sweat glands that cause the most discomfort with sweaty palms and feet. Every time you sweat, there’s a chance you’ll produce an unpleasant body odor. Some people are more susceptible to foul body odor than other people. Other factors that can affect body odor are: Exercise.

You can use cooked beets in salads, to make hummus or to blend into smoothies. They can be diced for slaw, quartered for a grain bowl or mashed to...
Read More »
Given below are a list of the drinks that make you lose weight, along with recipes to prepare them. Apple Cider Vinegar with Berries and Lemon....
Read More »
A scrumptious morning smoothy based on the diets of among the healthiest, longest-living hamlet in the world.
Learn More »
In most cases, people can safely eat beets or drink beetroot juice without experiencing any negative side effects. Drinking beetroot juice...
Read More »
Lemon water can promote fullness, support hydration, boost metabolism, and increase weight loss. However, lemon water is no better than regular...
Read More »
This effective juice jolts the metabolism, boosts energy and burns fat all day.
Learn More »Prescription medicines may prevent sweating. If your healthcare provider suggests this, they’ll caution you to be careful about using it because your body needs to sweat to cool itself when needed. There are some severe conditions that require surgery, which involves removing sweat glands from under your arms or preventing nerve signals from reaching your sweat glands.

Lifestyle and home remedies Drink more water, less alcohol. Alcohol is dehydrating and can lower blood pressure, even if drinking in moderation....
Read More »
around 4-8 weeks So, how long does it take turmeric to work? Depending on your body mass and condition, it will usually take around 4-8 weeks for...
Read More »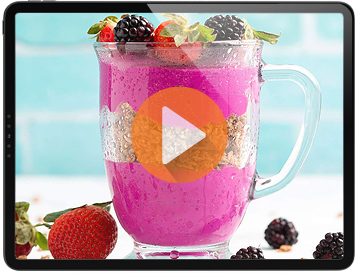
A potent powdered supplement blended right into water or your favored beverage to be appreciated as a scrumptious morning smoothy.
Learn More »
Spinach juice Spinach juice is a delicious way to reap most of spinach's health properties. The leafy veggie is an excellent source of potassium....
Read More »
This effective juice jolts the metabolism, boosts energy and burns fat all day.
Learn More »
In SCLC, amongst the important causes of low potassium levels in the blood are adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)-secreting tumors. Ectopic...
Read More »